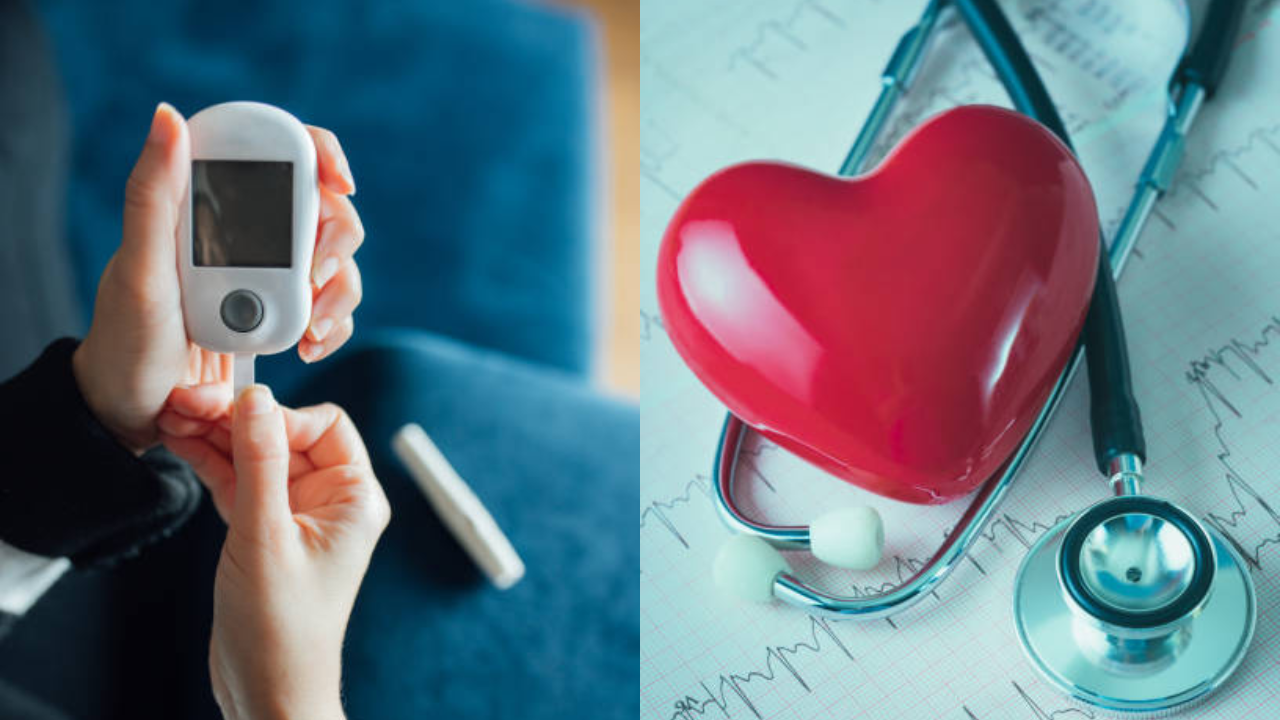
Know How Diabetes Impacts Your Heart Health
Photo : iStock
Diabetes is a disease wherein your blood sugar (glucose) levels are high. A person usually develops the condition when their pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin or no insulin at all or when their body doesn’t respond to the insulin that is produced by the pancreas. WHO says that uncontrolled blood sugar levels “over time leads to serious damage to many of the body’s systems, especially the nerves and blood vessels.”
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), there are estimated 77 million people above the age of 18 years are suffering from diabetes (type 2) and nearly 25 million are prediabetics in India. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) says that there are 537 million adults between 20 and 79 years old who are living with diabetes globally. This number is predicted to rise to 643 million by 2030 and 783 million by 2045.
World Diabetes Day is observed every year on November 14 and the day aims to raise awareness about diabetes and its preventive measures. In the initial stages, diabetes might not seem to be a major health issue. However, if the condition is not managed well, it can lead to major health issues such as chronic kidney disease, retinopathy, neuropathy, heart disease and others.
Here, take a look at how diabetes can affect your heart health.
High Blood Sugar and Blood Vessels
Persistent high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, thereby, making them stiffer and narrower. This restricts blood flow which makes the heart work harder and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Increased Cholesterol Levels
Diabetes often leads to higher levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol and lower levels of “good” HDL cholesterol. Increased LDL cholesterol leads to plaque buildup in the arteries which increases the chances of atherosclerosis. This is a condition that can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Diabetes is frequently accompanied by hypertension. High blood pressure adds strain on the heart and arteries, further increasing the risk of heart attack and heart failure. Both diabetes and hypertension are significant factors for heart disease.
Insulin Resistance and Inflammation
In people with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance can cause inflammation throughout the body. Chronic inflammation is known to be a risk factor for heart disease as it can lead to the development and rupture of arterial plaques, thereby, causing blockages.
Impact on Nerve Function
Diabetes can damage the nerves that control the heart and blood vessels which is a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. This damage can lead to an irregular heartbeat and in severe cases, may result in heart attack or heart failure.
Increased Risk of Heart Failure
With diabetes, the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently can be compromised which increases the risk of heart failure.