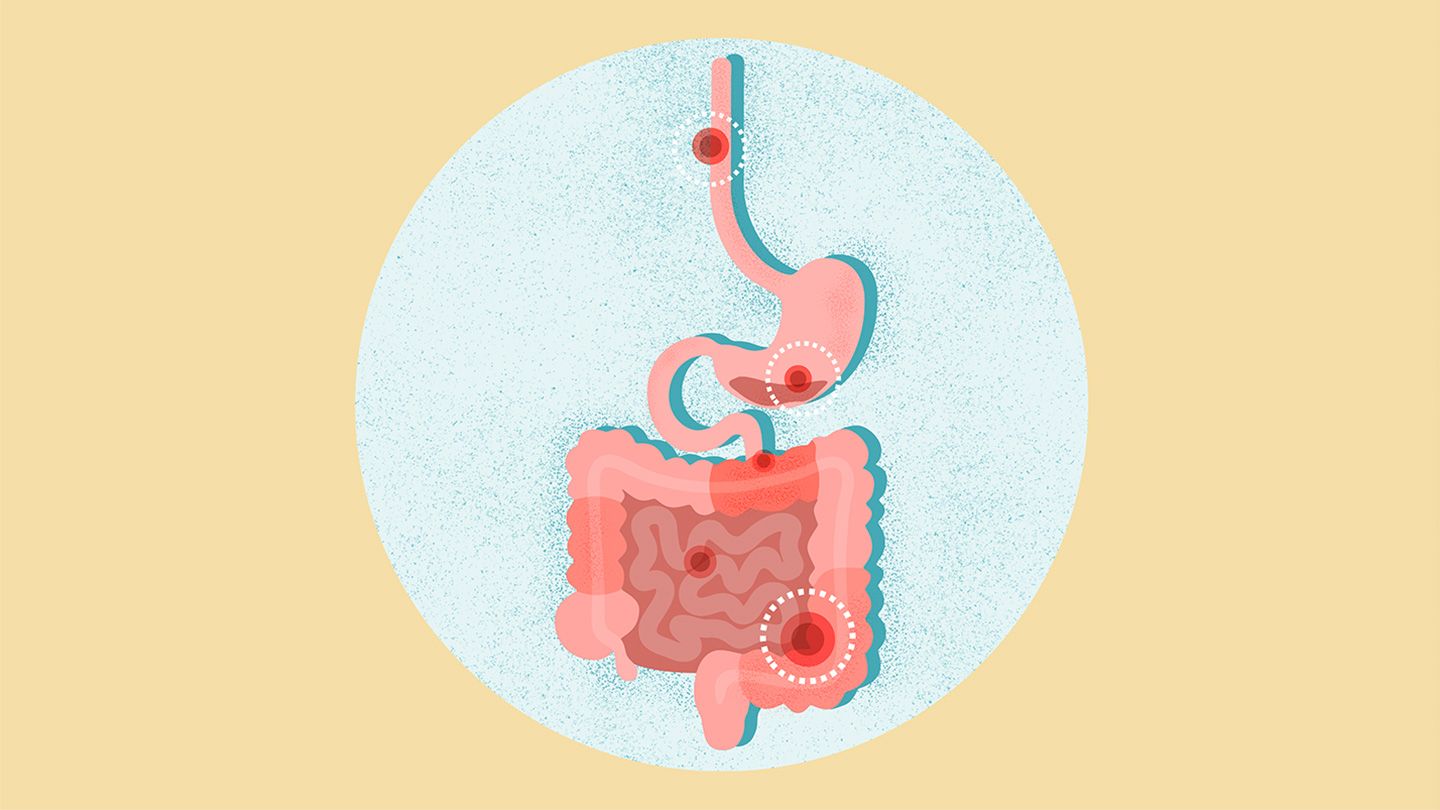
A gastrointestinal (GI) perforation is a hole or tear in the organs that move and digest food and drink in the body, like the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine (colon). Depending on the location, this hole can allow acidic stomach contents or stool (poop) to leak outside the GI system , causing pain and infection.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976298d068ad8-fc9c-49c3-94f8-95e23dc6b173 A GI perforation is a serious condition and usually requires antibiotics and surgery for full recovery.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976295f68abc2-90aa-4912-80b4-2041f891a0fe
Types of Gastrointestinal Perforation Types GI perforations are often categorized by their location: the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629ca8ffe18-b954-42ac-865a-8e910a6545d2 They can also be defined as contained or free:e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e59762934aa5a25-c5a0-4361-af0a-e2c2b9867644 Contained perforations: These are contained by other organs pushing against the hole. Free perforations: These allow gastric fluid or feces to spill into the abdominal cavity.
Signs and Symptoms of Gastrointestinal Perforation Symptoms When fluid from the GI tract leaks into the abdominal cavity, it can irritate the tissues it touches and cause severe inflammation called peritonitis. The most common symptom of a gastrointestinal perforation is abdominal pain , but sometimes symptoms can come on slowly, delaying a diagnosis. This is especially true for colonic perforations (also known as ruptured colon).e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976292ca97c86-c830-418f-a986-8c1dbd19667a Symptoms of a GI perforation may include:e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629562c383e-8940-411f-93bf-1ab58cabb84d Severe abdominal cramping and paine60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629420d8224-1aa7-4d19-ab2c-7b1d22f16023 Abdomen that’s painful to the touch Distended (swollen) abdomen Fever and chills Nausea and vomiting
Causes and Risk Factors of Gastrointestinal Perforation Causes Injury, trauma, and medical conditions can all cause GI perforation. Swallowing harmful chemicals, batteries, or sharp objects can increase the risk of puncturing a hole along the GI tract. Trauma from a car accident or weapon can also tear the stomach or intestines.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976297b48ec66-913d-410a-a236-174d5e580a58 Severe constipation can lead to a ruptured colon if stool builds up and gets stuck in the colon, and extremely forceful vomiting can cause stomach perforation. Some tears happen during medical procedures like surgery or colonoscopy, but these complications are rare.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629b78324cf-b880-4765-b9c1-1f9b3efc5fca Certain medical conditions can also increase the risk of GI perforation, including:e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629579d5ad9-5004-4f63-85b7-9328221c1924 Appendicitis Crohn’s disease Ulcerative colitis Diverticulitis Hernias Gallstones Cancers of the digestive system Peptic ulcer disease One study found additional factors that can increase your risk, including older age, diabetes, and taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and glucocorticoid medications like prednisone.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629e9819491-b058-4bb7-b6db-de6abd38a8ac Location also matters: Ulcers in the uppermost part of the small intestine (the duodenum) cause perforation up to three times more often than stomach ulcers do. Diverticulitis causes 15 percent of all colon perforations, and in older adults, a perforated appendix is the most common cause.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976297b310589-f4c5-4ead-b51f-e1e4e029287f
How Is Gastrointestinal Perforation Diagnosed? Diagnosis To diagnose a GI perforation, a healthcare provider will do a physical exam; ask about your symptoms; check your vital signs like blood pressure, temperature, and heart rate; and order blood or imaging tests if needed.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629f5bbbf5f-1519-41b5-adae-11541b3e7fb2 Tests used to diagnose gastrointestinal perforation may include:e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629e61aea86-6d7e-45cf-9e58-d3994ad05854 Blood tests , which can reveal signs of infection and inflammation and check how well your kidneys and liver are workinge60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976290ec556d8-1498-469a-bc5b-15d2afb8e6a2 X-rays , which reveal free air around the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, a potential symptom of perforation Computed tomography (CT) scans , which provide detailed images to help a provider locate the tear Colonoscopy , which allows a provider to see the inside of the large intestine with a small camera Endoscopy , which uses a small camera to show the inner lining of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine
Treatment and Medication Options for Gastrointestinal Perforation Treatment Treatment for Gl perforation starts with getting fluids through an IV and monitoring you for a full-body infection called sepsis , or shock, a life-threatening complication that blocks oxygen delivery throughout the body.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976295763c0d1-d234-4bd6-8ad2-e046f377afc6 You won’t be able to eat or drink anything, and you may need a nasogastric tube (a tube inserted through your nose and into your stomach) hooked up to suction to remove stomach contents and decompress the GI tract.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629e762c6e3-edbe-4861-8fe2-fa3c17ea4e90 Once these things are in place, other treatments can be started, including medications and surgery. Medication GI perforation is typically treated with antibiotics , often given through an IV to fight infection from the leak.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e59762923b19a58-056e-4986-97ad-5f0bfb6842dd Even if you have surgery, you may need to take these medications for several weeks. It’s important to take each dose for the full course to avoid a returning infection.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976290b5b309e-ead3-4bc4-b3dd-219538e785f6 Typically, antibiotics are given alongside surgery, but in rare cases, antibiotics alone can keep infection at bay while your body heals itself.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629d24a1e3c-4448-4006-aa3d-5376d1be06cb Surgery In most cases, GI perforation requires surgery for repair. For anyone who’s otherwise stable and showing no signs of sepsis, surgeons may opt for a minimally invasive surgery, like an endoscopic procedure or a laparoscopy. Endoscopic repair typically requires no incisions, and the surgeon can close up the hole or tear from inside the GI tract.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976294644086a-f289-49f4-b164-91dbd3dfcf22 A laparoscopy involves a few small incisions in the abdomen through which the surgeon inserts a camera and specialized tools to identify and repair the hole. However, if you have other symptoms pointing to sepsis or shock, you may need emergency surgery and an open exploration with a larger incision (a laparotomy), so the surgeon can see what they need to see more quickly.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976299922b587-0fb7-4ee1-a54e-b707198eefa3 Depending on the extent of inflammation and damage to the surrounding areas, the surgeon sometimes must remove parts of the intestine. This is known as a colectomy . In some cases, the intestine can be reattached.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629a5ebc232-28bb-4234-8b25-f6aaf96dde81 Other times, the surgeon must make a small incision in the abdomen and pull the intestine out through it to make a stoma. This allows feces to come out that way into a bag (a colostomy or ileostomy ) instead of through the rectum.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e59762919e7a410-063c-4a65-843d-2b01814f9d9e Ostomies can be temporary and may be removed after healing.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629cc760502-f39d-4fa4-8661-07b2971fd8ea
Prevention of Gastrointestinal Perforation Prevention Prevention of GI perforation may not always be possible, but you can lower your risk with these habits:e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629353b71c3-f9e1-4b94-bff6-07ce4f87c61b Avoid smoking or use of any tobacco products. Limit the use of NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Advil) and naproxen (Aleve).e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976292ef9d9d4-72ae-4dd0-8691-87eb538cc7be Include plenty of fiber in your diet to avoid constipation, which can raise your risk of GI perforation. See your healthcare provider on a regular basis, especially if you have a health condition. If you’ve had a GI perforation, it’s important to report any new abdominal pain right away to help prevent serious complications. If your provider can catch a perforation early, your treatment can be much simpler and quicker.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976290764196d-8a5a-40aa-aca3-2d93b6e5bacb
Lifestyle Changes for Gastrointestinal Perforation Lifestyle Changes Lifestyle changes for GI perforation are similar to the prevention strategies noted above. To keep your risk of perforation low, don’t smoke, use tobacco products, take NSAIDs on a regular basis, or eat too little fiber.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976299dfc7499-d26d-4cc2-93c8-b5a9a89c7e85
Gastrointestinal Perforation Prognosis Prognosis and Outlook GI perforation is a serious, life-threatening condition, but with prompt treatment, most people recover fully after several weeks. Research suggests the survival rate for GI perforation is about 90 percent.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629046ccadf-cd39-4f14-960f-eb467843a198 Your prognosis depends heavily on how long you have the perforation before treatment begins, and complications like sepsis can lower your chances of successful recovery. So, if you experience GI perforation symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629f636e9a8-9645-467e-b9e1-08cd1fd808c1e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629265ce5e7-ce8f-4108-9aab-a4d1c82036e1
Complications of Gastrointestinal Perforation Complications As mentioned, GI perforation can sometimes come with complications. They may include:e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629d14e3735-e2b9-44f4-9abd-b65cc78fb6b3 Impaired blood flow to major organs Internal bleedinge60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976295bb9f002-3d52-4421-8649-005a13a02c6c Peritonitis (inflammation of abdominal wall) Infection Sepsis e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629f691eb45-fc5e-4a41-8f1a-0d91c75f8093 Organ failure Delayed wound healing Post-surgical bowel obstruction Fistulas Hernias
Research and Statistics: Who Has Gastrointestinal Perforation? Research and Statistics GI perforations are rare. They happen in only 1 to 3 percent of people overall.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e59762948dba760-9f92-497d-a53b-c935c4f76e8d One small study of 140 people with GI perforation found the most common age group for this condition was 41 to 60 years old. In this study, men were also more likely to have a perforation than women.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e597629f21bf8a6-da83-41f6-ab32-487fd0f90e06 In a review of 838 cases of bowel perforation, one study found that most were caused by blunt trauma during a motor vehicle accident, especially in seat-belt users.e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e5976299c972594-695d-4089-b122-e85b0120e096
Related Conditions Related Conditions Some medical conditions can have similar symptoms to gastrointestinal perforation, including:e60dc2a1-f33c-4a05-9b50-8e3e8e59762978c39dae-f1ef-4220-b0ee-2b723596fd10 Inflammatory bowel diseases ( IBD ), such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis Cholecystitis (gallbladder inflammation) Gastritis (stomach inflammation) Pancreatitis Appendicitis Constipation Endometriosis Fallopian tube-related conditions
The Takeaway Gastrointestinal perforation is a tear or hole in the organs of the GI tract, including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine (colon.) This serious medical condition can be caused by trauma to the GI area, severe constipation, extremely forceful vomiting, or other GI conditions. The most common symptom of gastrointestinal perforation is abdominal pain; other symptoms include a swollen abdomen, fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. Quick treatment with antibiotics and surgery are essential for recovery. If you experience any symptoms of gastrointestinal perforation, seek medical care immediately.
Resources We Trust Cleveland Clinic: Gastrointestinal PerforationMayo Clinic: PeritonitisNational Health Service: Ulcerative Colitis ComplicationsCrohn’s & Colitis Foundation: Intestinal ComplicationsMedlinePlus: Gastrointestinal Perforation
What Is a Gastrointestinal Perforation?
- June 10, 2025
- 0 Comments
- 10 Views
- Read in 12 Minutes