Myositis and the Role of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Myositis is a rare autoimmune disease characterised by chronic muscle inflammation. The condition can lead to muscle weakness, pain, and overall fatigue, impacting daily life significantly. Samantha shared that her anti-inflammatory diet is crucial in maintaining a stable weight that benefits her overall health and helps manage myositis symptoms. “Yes, another weight comment… I am on a strict anti-inflammatory diet required for my condition, which prevents me from putting on weight,” she wrote on Instagram. “Stop judging people and let them be. Live and let live, guys, please, it’s 2024.”
How an Anti-Inflammatory Diet Supports Myositis Management
An anti-inflammatory diet can be a powerful tool for those dealing with inflammatory conditions like myositis. This dietary approach emphasises whole, nutrient-rich foods that reduce inflammation and boost the body’s immune response. Foods that support anti-inflammatory responses are rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, fibre, and essential vitamins and minerals, all of which can help to reduce inflammation over time.
Also Read: Fatima Sana Sheikh Opens Up About Epilepsy Diagnosis; Here’s Everything To Know About It
For myositis patients, managing inflammation is critical. The immune system’s attacks on muscle tissue lead to increased pro-inflammatory compounds, such as cytokines and free radicals, which can cause oxidative stress. This results in muscle degeneration, as chronic inflammation weakens the muscle tissues over time. By incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, individuals like Samantha can potentially decrease these inflammation markers, supporting muscle health and overall well-being.
What Foods Are Key to an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
The anti-inflammatory diet Samantha follows likely includes nutrient-dense foods while avoiding ingredients known to trigger inflammation. Here’s a closer look at foods beneficial to those with myositis:
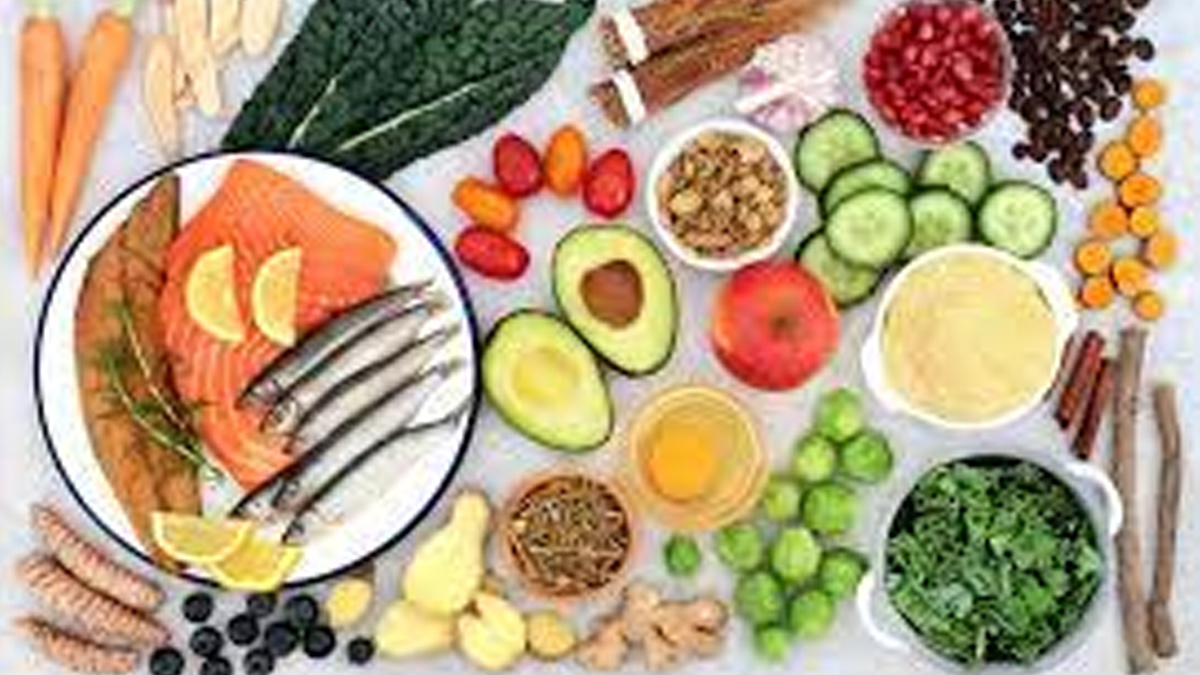
- For Vegetarians: Vegetables and fruits like leafy greens, berries, and cruciferous vegetables (such as broccoli and cauliflower) are high in antioxidants and fibre. Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice, along with nuts, seeds, and spices like turmeric and ginger, provide essential nutrients and compounds that can reduce inflammation.
- For Non-Vegetarians: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which combat inflammation. Eggs and skinless chicken provide protein without the saturated fat found in red meats, making them better choices for maintaining muscle health.
Both vegetarians and non-vegetarians can benefit from healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil and avocados, which have monounsaturated fats known to reduce inflammatory markers.

Avoiding Foods that Exacerbate Inflammation
To follow an anti-inflammatory diet, it’s essential to avoid foods that can trigger or worsen inflammation. Samantha’s diet excludes processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats—all of which can increase inflammation and oxidative stress. Sugary foods, for example, cause blood sugar spikes that lead to inflammation, while processed foods often contain refined oils and additives that further stress the immune system. For those managing myositis, these foods can intensify symptoms and hinder the diet’s effectiveness.
Red and processed meats, often high in saturated fats, can elevate inflammatory markers if eaten in excess. Alcohol, another trigger for inflammation, is often limited or avoided entirely in an anti-inflammatory diet. Samantha’s disciplined approach serves as a reminder of the importance of consistency in managing dietary triggers to support long-term health outcomes.
Balancing Nutritional Needs on an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
For anyone on a restrictive diet, ensuring balanced nutrition is essential. An anti-inflammatory approach can meet most nutritional needs but requires careful monitoring to avoid deficiencies. Protein intake, vital for muscle health, can be managed by combining plant-based sources with lean animal proteins. Healthy fats, including omega-3s from fatty fish or seeds and monounsaturated fats from olive oil, play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and should be a staple in anti-inflammatory diets.
For individuals like Samantha, whose condition demands careful attention to weight and muscle health, such a diet must also account for micronutrients. This balance helps prevent the unintentional loss of muscle mass, a risk for those with myositis.
Samantha’s Journey as an Advocate for Health and Positivity
By speaking up about her condition and her lifestyle changes, Samantha Ruth Prabhu has become a voice for those managing chronic illnesses. Her transparency in addressing the challenges of living with myositis, including the effects on her weight, not only normalises the conversation around health struggles but also highlights the power of food as a form of medicine. Her journey underscores the importance of a supportive community, especially when managing an illness that affects both physical and mental well-being.
As Samantha continues to inspire her fans with her resilience, her message reminds us all to refrain from judging others and to prioritize health over appearance. Through her story, she shows that wellness is more than just a physical state; it’s a lifestyle that requires patience, discipline, and a positive outlook.