1 / 10
1 / 10Understanding Chronic Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a long-term health issue that can be influenced by diet. According to a Johns Hopkins University report, it is linked to diseases such as heart disease and diabetes and can be managed, to an extent, by what we choose to eat daily. (Pixabay image)
 2 / 10
2 / 10Types of Inflammation: There are two main types of inflammation. Acute inflammation is the body’s temporary response to injuries like cuts or infections. This usually resolves on its own. However, systemic inflammation can become chronic, lasting months or even years. (Pixabay image)

 3 / 10
3 / 10Diseases Linked to Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is associated with several serious health conditions, including obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. Research suggests that inflammation is a contributing factor in the development of these conditions. (Shutterstock image)

 4 / 10
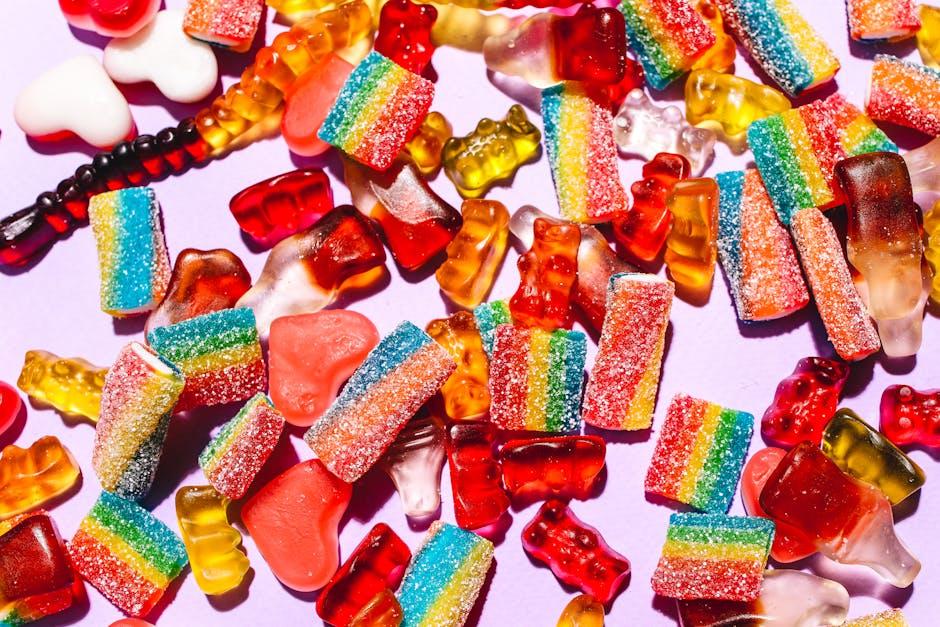
4 / 10Inflammatory Food Triggers: Diet plays a key role in managing inflammation. Certain foods are known to trigger inflammation, including red and processed meats, sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, and foods high in added sugars. (Pixabay image)

 5 / 10
5 / 10Cooking Method Matters: The way food is cooked can also impact inflammation levels. Grilling meats, for example, produces compounds linked to cancer risk. Healthier methods like baking, steaming, or stir-frying are better options to avoid triggering inflammation. (Pixabay image)

 6 / 10
6 / 10Check Processed Food Labels: Many processed foods contain hidden sugars and trans fats, which can contribute to inflammation. Reading ingredient labels is essential to identifying these ingredients and choosing healthier alternatives. (Pixabay image)

 7 / 10
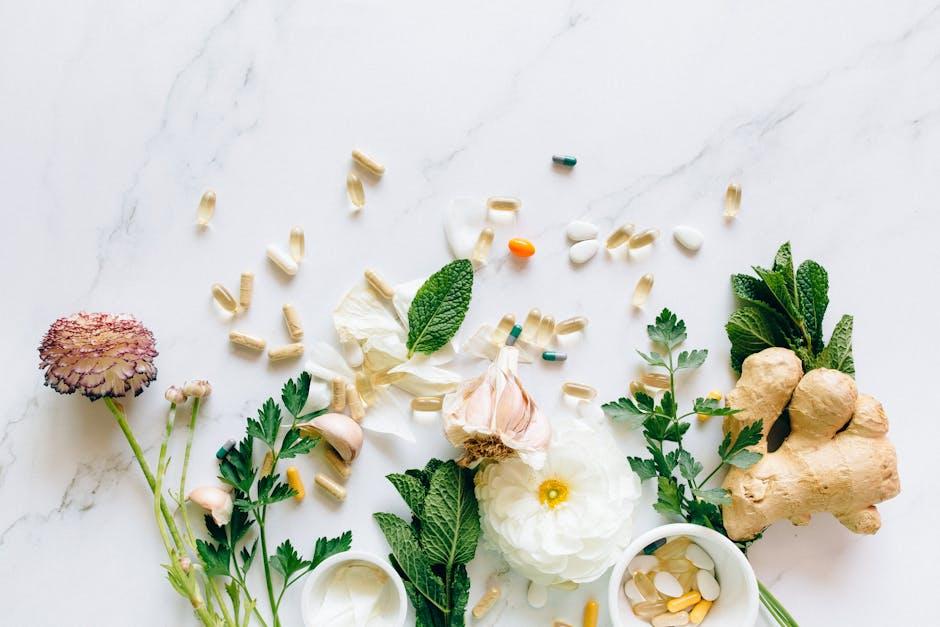
7 / 10Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Certain foods can actively reduce inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel have been shown to fight inflammation. For vegetarians, nuts, seeds, and canola oil also offer similar benefits. (Pixabay image)
 8 / 10
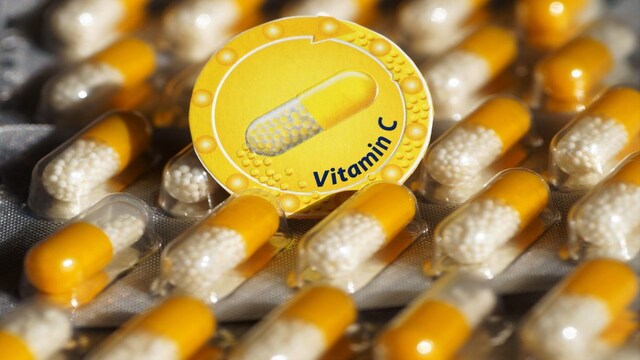
8 / 10Vitamin C Benefits: Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant, helps the body manage inflammation by protecting cells from damage. Common sources include citrus fruits, bell peppers, and leafy greens, making them key to an anti-inflammatory diet. (Pixabay image)

 9 / 10
9 / 10Polyphenols and Colourful Diets: Polyphenols, naturally occurring compounds in colourful fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, help protect the body from inflammation. Tea, coffee, and dark chocolate also contain these beneficial compounds. (Reuters photo)

 10 / 10
10 / 10Simple Diet Changes: Switching to a Mediterranean-style diet, which emphasises whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins, can help manage inflammation. Gradual changes, like substituting unhealthy foods for nutritious ones, can make a difference over time. (Pixabay image)